Horizontal vs. Vertical Acquisition: How to Choose the Right Acquisition Strategy
September 19, 2024 Written by Cynthia Orduña

Compare Providers
Download our outplacement comparison sheet
Request Pricing
Compare our rates to other providers
Are you thinking about acquiring another business? You might already know the potential benefits, such as reducing costs, scaling your operations, diversifying your products, or expanding into new markets. It’s also important to choose the type of acquisition that would be most beneficial. Like many companies, you’re probably weighing the pros and cons of horizontal vs. vertical acquisitions.
While these two types of acquisitions are popular, the differences between them are often misunderstood by businesses, even though they are distinct approaches. If you’re facing the same confusion, don’t worry. We’ve compared both types of acquisitions side by side. Read on to see how the horizontal vs. vertical acquisition showdown plays out.
What Is the Difference Between Horizontal and Vertical Acquisition?
The primary distinction between horizontal vs. vertical acquisitions lies in their objectives.
What Is a Horizontal Acquisition?
A horizontal acquisition occurs when the two companies that are merging offer the same products or services, operating at the same production level.
In this case, the acquired company is typically a direct competitor of the acquiring company. The key motive behind a horizontal acquisition is to eliminate competition. This leads to several advantages, including increased market share, reduced costs, and higher revenue and profit.
What Is a Vertical Acquisition?
In contrast, a vertical acquisition involves a company acquiring another business within the same industry, but at a different stage of production or with different products or services along the same value chain.
The goal of a vertical acquisition differs significantly from that of a horizontal one. While horizontal acquisitions focus on reducing costs and boosting profits, the primary aim of a vertical acquisition is to secure a stable supply of essential goods, prevent supply chain disruptions, and limit access to key resources for competitors.
If you are actively considering either a horizontal or vertical acquisition soon, click below to download our free mergers and acquisitions success guide to make sure you’re prepared to smoothly navigate the entire process from start to finish.
How to Decide Between Horizontal vs. Vertical Acquisition for Your Organization
Given these differences, it’s important to assess all of the key aspects when deciding between a horizontal or vertical acquisition. One critical question to consider is this: Are you aiming to expand the size of your business, or is your priority to strengthen the supply chain?
Additionally, there are two key factors to evaluate when determining which type of acquisition is right for you:
1. Self-Sufficiency
One major difference between horizontal vs. vertical acquisitions is the level of control and self-sufficiency they provide. Would you prefer to manufacture the components of your products in-house, or rather rely on external vendors to supply these components?
With a vertical acquisition, you gain more control over the entire production and distribution process. This allows you to increase profits by eliminating intermediaries and potentially lowering production costs over time. You can also create custom components specialized for your products, which enhances efficiency and reduces waste.
However, vertical integration requires significant financial, organizational, and operational resources, and setting up a smooth production process can be time-consuming and costly. Before committing, assess whether your organization is ready to take on this responsibility.
On the other hand, a horizontal acquisition is less about self-sufficiency and more about synergy. It allows you to focus on your final product while outsourcing parts of the production process to external vendors. This reduces risks, as access to multiple suppliers serves as a safety net if issues arise with one vendor. However, this reliance on external sources can also limit your control over production and manufacturing.
Ultimately, your decision should depend on whether you want to control every aspect of production and distribution or delegate that to outside vendors. A vertical acquisition enhances self-sufficiency with greater control over production and manufacturing, while a horizontal acquisition focuses on synergy and efficiency. Before making your final decision, ask yourself which of these you want to prioritize for your organization.
2. Diversification
Another key difference between horizontal vs. vertical acquisitions is how they impact diversification and concentration.
Horizontal acquisitions allow you to diversify by expanding your product range, combining your offerings with those of a competitor. This strategy enables you to increase the variety of your products or services, tap into new market sectors, and expand into broader geographic regions.
A vertical acquisition is more about refining and concentrating on your existing product range and value chain. By acquiring a company at a different stage or piece of the production process, you increase the cost-efficiency and value proposition of your specific offerings, while gaining more control over the greater industry beyond your individual market segment.
Before making your choice, consider this question: Do I want to diversify my product range, or focus on refining my existing products?
Horizontal vs. Vertical Acquisition: Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages and disadvantages of horizontal vs. vertical acquisitions set these two strategies apart, offering unique benefits and challenges for each path.
Advantages of Horizontal Acquisitions
- Elimination of direct competitors: By acquiring competitors, you can reduce competition and gain a larger market share.
- Improved product focus: Merging with a company in the same industry allows you to streamline and enhance product offerings.
- Economies of scale: A larger operation can lead to cost savings through bulk production and increased efficiency.
- Ease of management: Managing a horizontal acquisition is simpler due to the similarity in products and processes between the companies.
Disadvantages of Horizontal Acquisitions
- Limited innovation: The focus on similar products may reduce flexibility and hinder the introduction of new ideas.
- Legal challenges: Horizontal acquisitions can raise antitrust concerns, leading to potential legal repercussions.
- Decentralized structure: Integrating two similar companies can create inefficiencies, decentralizing operations and negatively impacting productivity.
- Potential personnel overlap: Acquiring similar product teams increases the likelihood of staff redundancies that could necessitate laying off some of the workforce.
Advantages of Vertical Acquisitions
- Greater control over the value chain: Vertical integration allows you to manage the entire production and distribution process, from raw materials to finished products.
- More cost control: Acquiring companies at different stages of production helps you control costs throughout the supply chain.
- Improved supply chain coordination: You can optimize transportation and other supply chain logistics, increasing your overall efficiency.
- Exclusive resource access: It allows you to block competitors from accessing key resources or markets, giving you a more competitive edge.
Disadvantages of Vertical Acquisitions
- Scaling difficulties: Vertical integration can limit your ability to scale production quickly due to increased complexity in managing different stages of production.
- Market entry barriers: Entering new sectors through vertical acquisition may introduce significant barriers that you are less familiar with navigating.
- Higher capital investment: Vertical acquisitions require more substantial financial resources to manage different areas of the business.
- New industry knowledge: It may require learning the operations of a new sector, adding more complexity for your workforce and business model.
- Internal confusion: Managing a broader range of processes can cause confusion and inefficiencies within the organization, leading to decreased productivity and morale.
Horizontal Integration Examples
Here are some real-life examples of horizontal acquisitions that illustrate how companies have strategically expanded their reach and influence within their respective industries:
- Meta acquires Instagram: Meta’s acquisition of Instagram in 2012 is a well-known horizontal acquisition. Both companies were in the social media space, providing similar services for photo and content sharing, and thus operating at the same industry level.
- Disney acquires 21st Century Fox: In 2019, Disney purchased 21st Century Fox, combining two media and entertainment giants. This acquisition allowed Disney to increase its content library, expanding its dominance in the entertainment industry.
- Marriott acquires Starwood Hotels: In 2016, Marriott acquired Starwood Hotels in a horizontal acquisition. Both companies operated in the hospitality industry, offering similar services, which helped Marriott expand its market share and customer base.
Vertical Integration Examples
Now let’s look at three notable real-life examples of vertical acquisitions:
- Amazon acquires Whole Foods: In 2017, Amazon acquired grocery chain Whole Foods. This vertical acquisition allowed Amazon to integrate its e-commerce and distribution capabilities with a physical food retail network, gaining more control over its supply chain and distribution channels.
- Tesla acquires SolarCity: Tesla’s 2016 acquisition of SolarCity is another example of a vertical acquisition. Tesla, an electric car manufacturer, acquired SolarCity, a solar energy company, to integrate renewable energy solutions into its energy products, gaining more control over the greater energy infrastructure.
- Apple acquires Dialog Semiconductor: Apple bought a major portion of chip manufacturer Dialog Semiconductor in 2018 to ensure a stable supply of power management technology for its devices, helping Apple maintain control over critical components in its supply chain.
Horizontal vs. Vertical Acquisition: Key Takeaways
A business acquisition involves acquiring another company along with its assets. Companies pursue acquisitions to leverage existing strengths and address their own weaknesses. This growth strategy can produce significant long-term benefits. To maximize the value of an acquisition, it’s important to differentiate between horizontal and vertical acquisitions and determine which type best aligns with your objectives.
Here are the key takeaways:
- Acquisitions aim to reduce costs, scale operations, diversify products, and expand into new markets.
- Deciding between horizontal vs. vertical acquisitions depends on whether you want to expand market presence or enhance supply chain control.
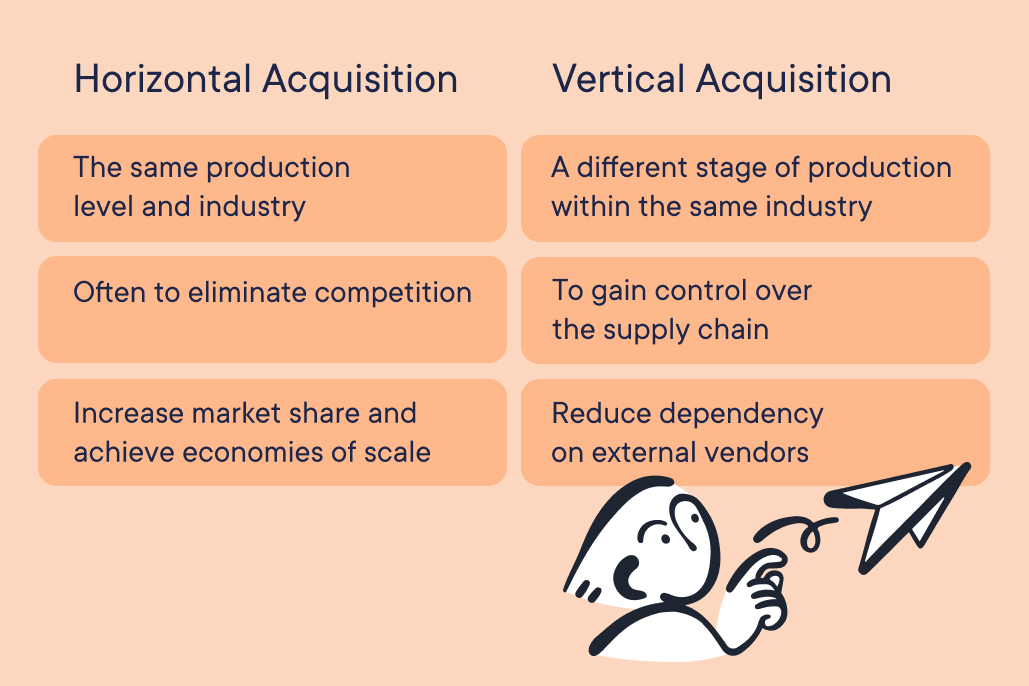
- Horizontal acquisition involves merging with a company at the same production level and industry, often to eliminate competition, increase market share, and achieve economies of scale.
- Vertical acquisition involves acquiring a company at a different stage of production within the same industry to gain control over the supply chain and reduce dependency on external vendors.
- The advantages of horizontal acquisition are elimination of competition, improvement of product focus, achievement of economies of scale, and simplified management.
- The disadvantages of horizontal acquisition are limited innovation, potential legal challenges, possible inefficiencies due to decentralization, and personnel redundancies that could necessitate layoffs.
- The advantages of vertical acquisitions are greater control over the value chain, more cost control, improved supply chain coordination, and exclusive resource access.
- The disadvantages of vertical acquisitions are scaling difficulties, market entry barriers, high capital investment, and potential internal confusion.
At Careerminds, we believe that you can never be too prepared for your next major business event, especially any that might result in workforce integrations and reductions. Our arsenal of resources, templates, guides, and industry-leading outplacement services can help you navigate the delicate integration or reduction process. Click below to speak with one of our experts and see if we are the right partner for your organization.
In need of outplacement assistance?
At Careerminds, we care about people first. That’s why we offer personalized talent management solutions for every level at lower costs, globally.



